Disassembly, Fully Digitalized
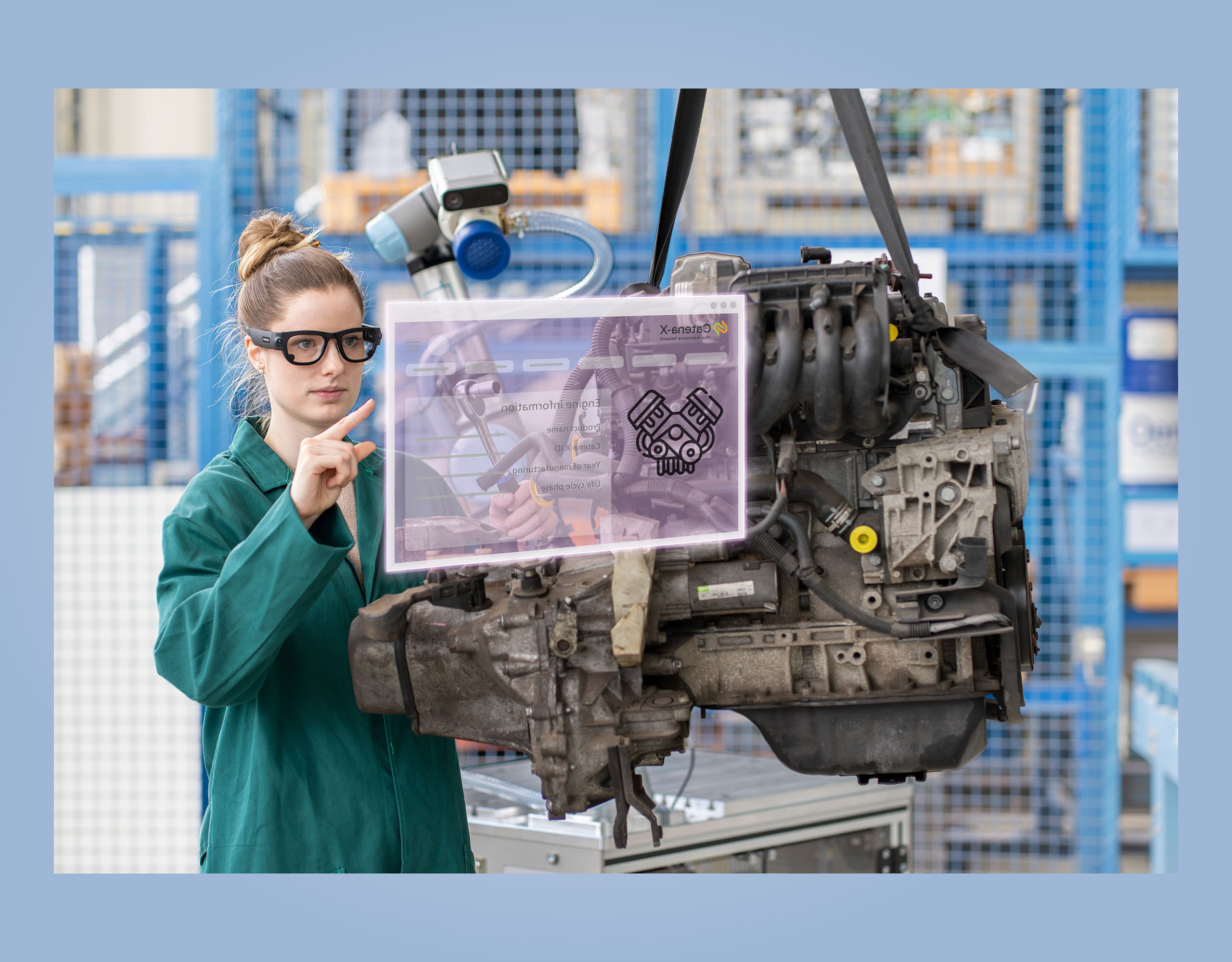
Researchers at Fraunhofer IPK have developed a comprehensive and coherent digitalization concept for the disassembly of vehicles. At the heart of this concept is the Circular Economy Assistant, a decision-making tool designed to make companies fit for the circular economy. The CE Assistant also provides a straightforward overview of various disassembly options and their individual carbon footprints, making it stand out thanks to integrated solutions that cover the entire disassembly process.
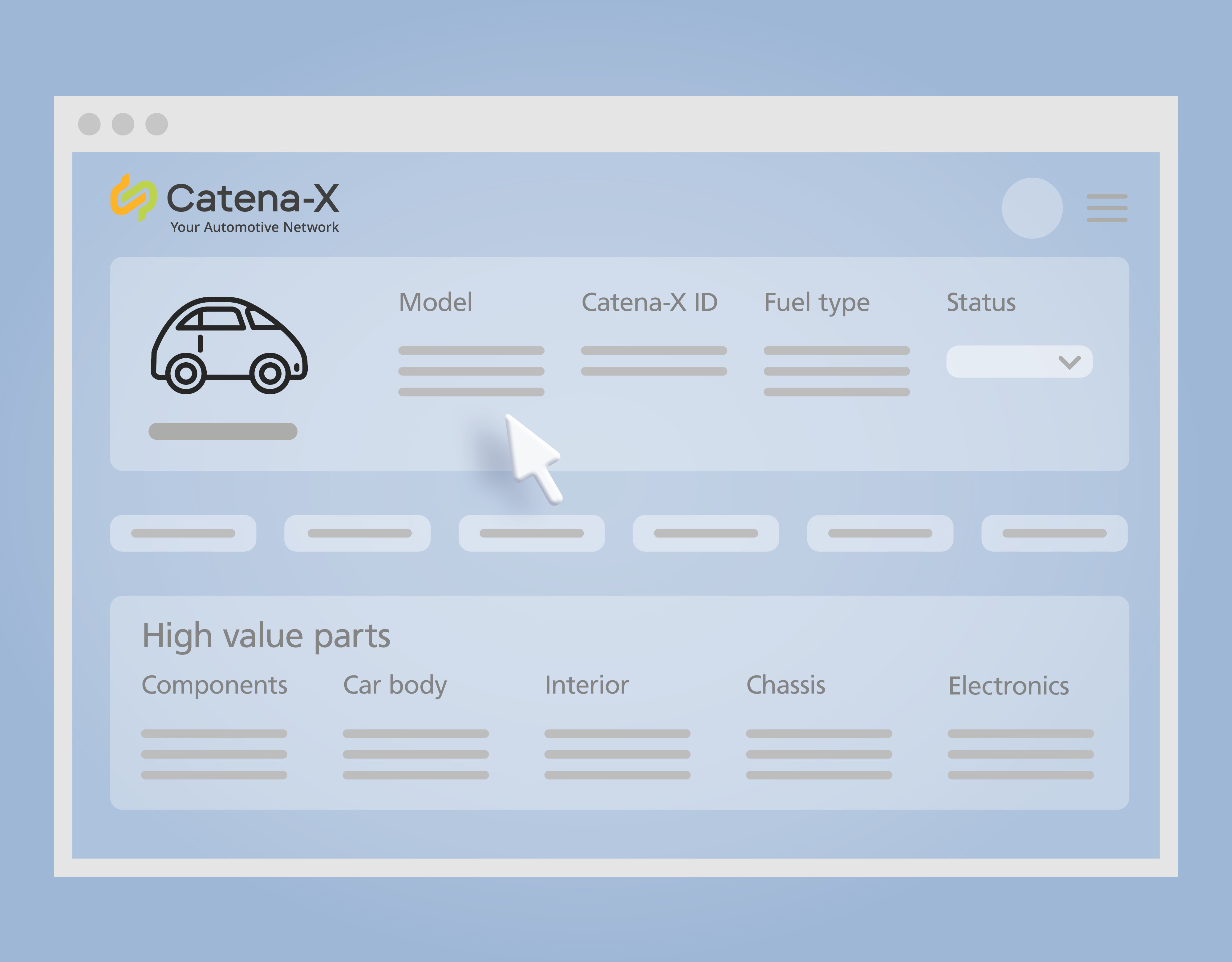
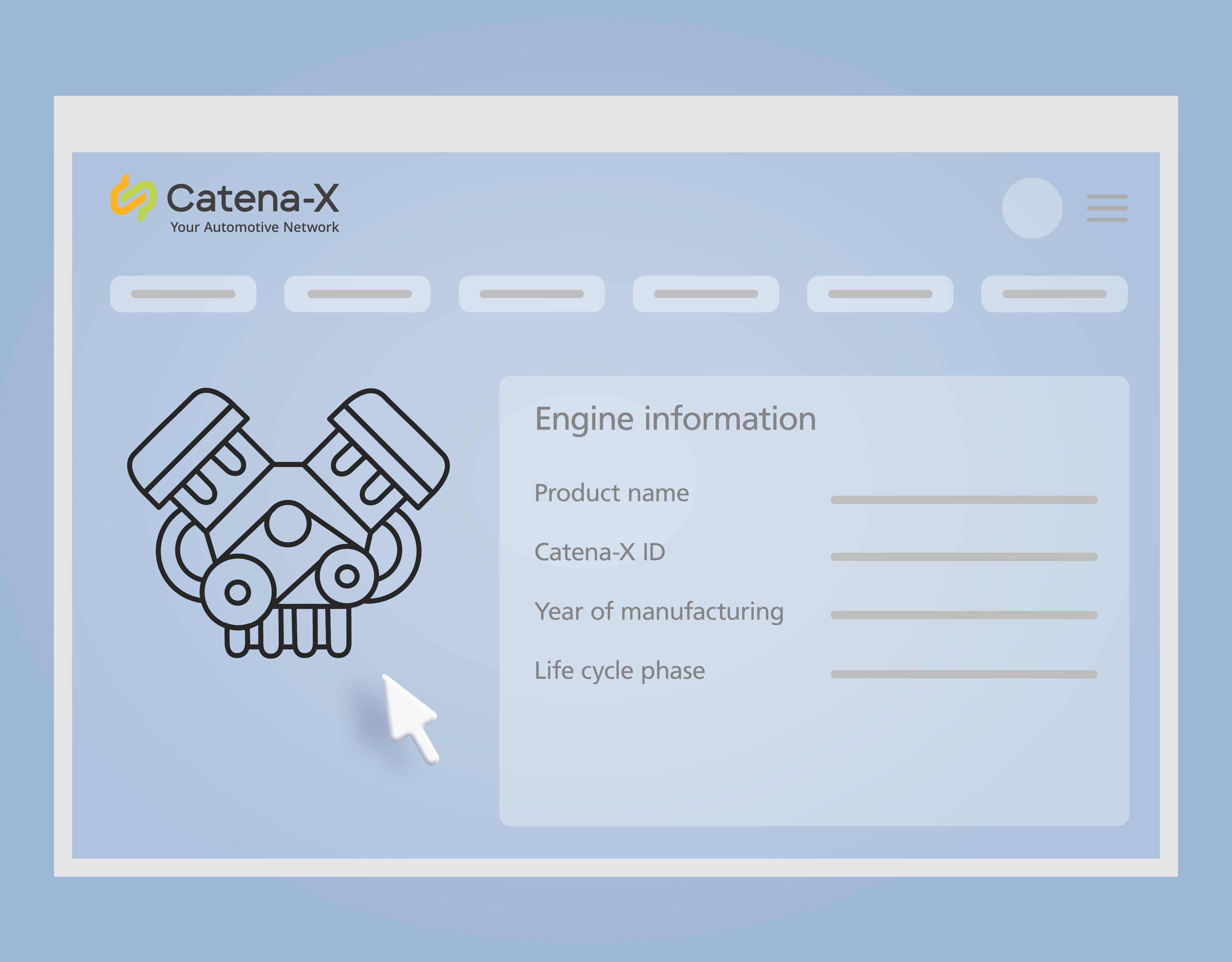
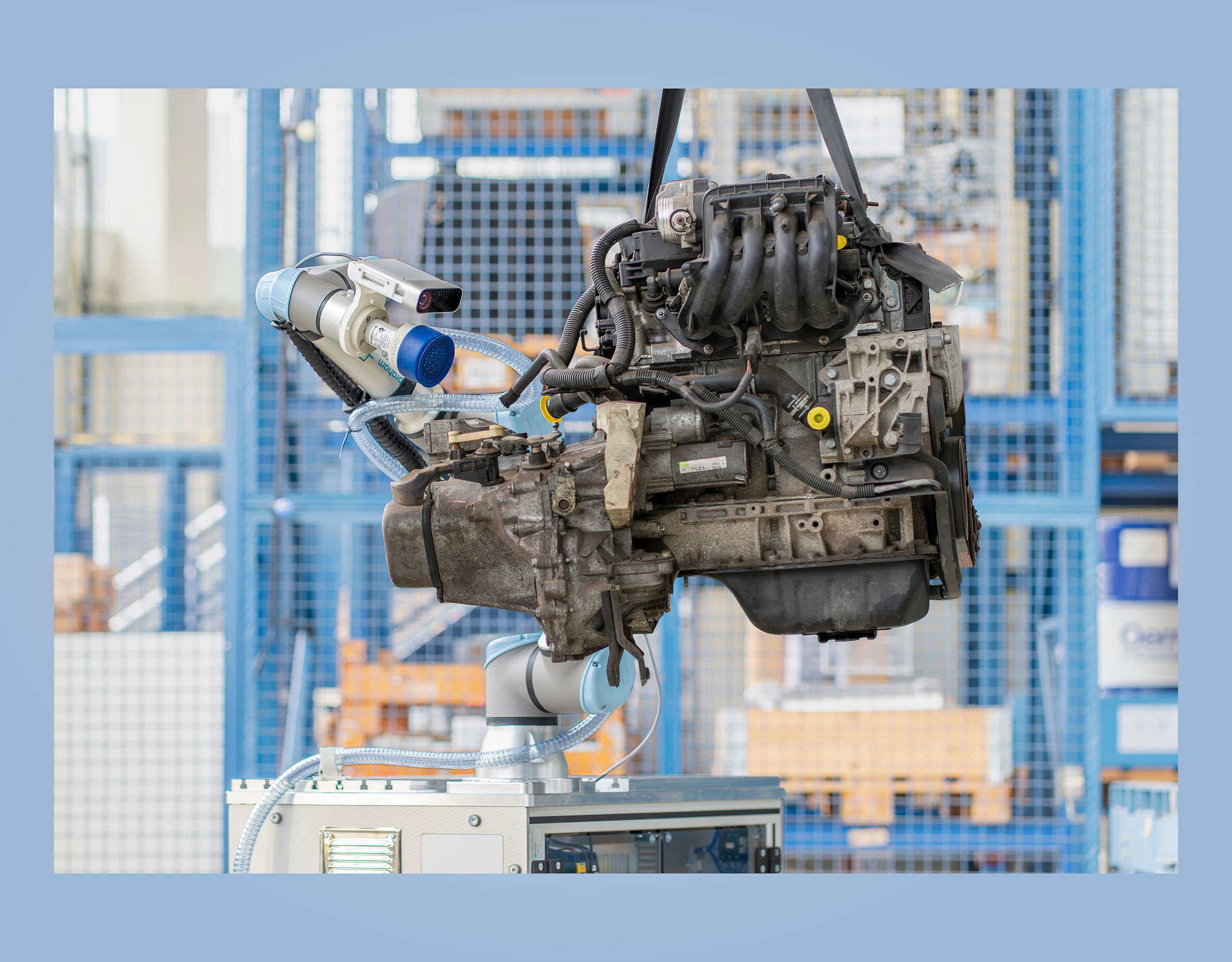

Next stop: automation
The digitalized disassembly process shown here has not yet reached the end of the road. After all, the demands on disassembly are growing: Increasingly complex vehicle components have to be taken apart so that the individual parts can be recycled. To make this possible even when skilled specialized workers are hard to come by, further automation measures are needed. To accomplish this, AR glasses are used during the disassembly process to capture images that can be used to train an AI. On the basis of this multimodal data recording, robots will be able to perform the strenuous manual work in the future.
You might also be interested in:
- More articles on the »Mobility of the Future«
- More information about the data ecosystem Catena-X
- Digma-DT - Digital Twins for Sustainability in the Automotive Sector
- Sustainability Into Industry [Article from »Solutions from Research and Development 2024 / 2025«]
- Software-driven Smart Dismantling [FUTUR article from the issue on »Data«]
 Fraunhofer Institute for Production Systems and Design Technology
Fraunhofer Institute for Production Systems and Design Technology