Digital Welding in the Age of Industry 4.0
Highly efficient and responsible production. Welding technology offers many opportunities to make processes more climate-neutral – in the digital world and in the real world.
Welding is so versatile: The world of welds – an overview
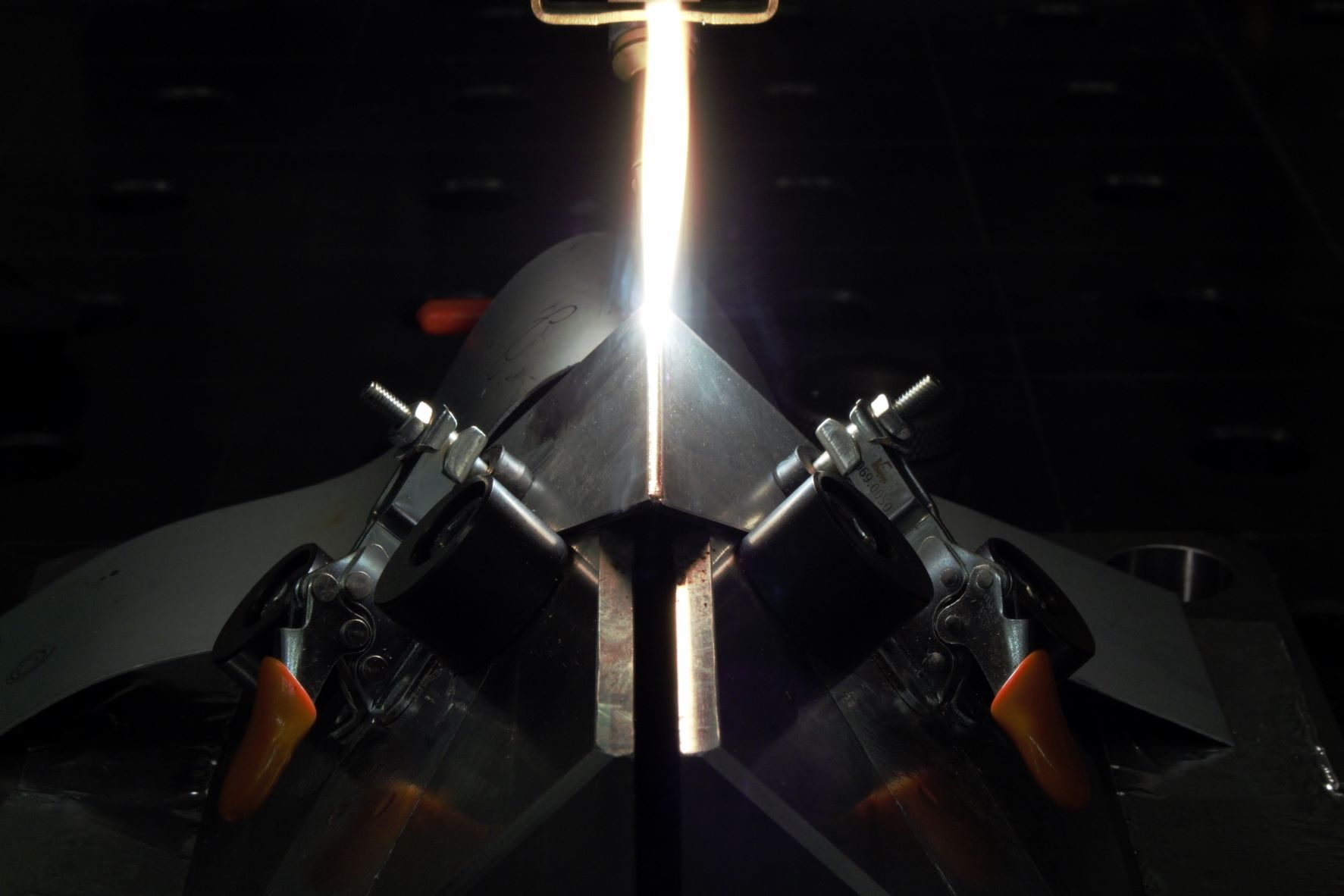

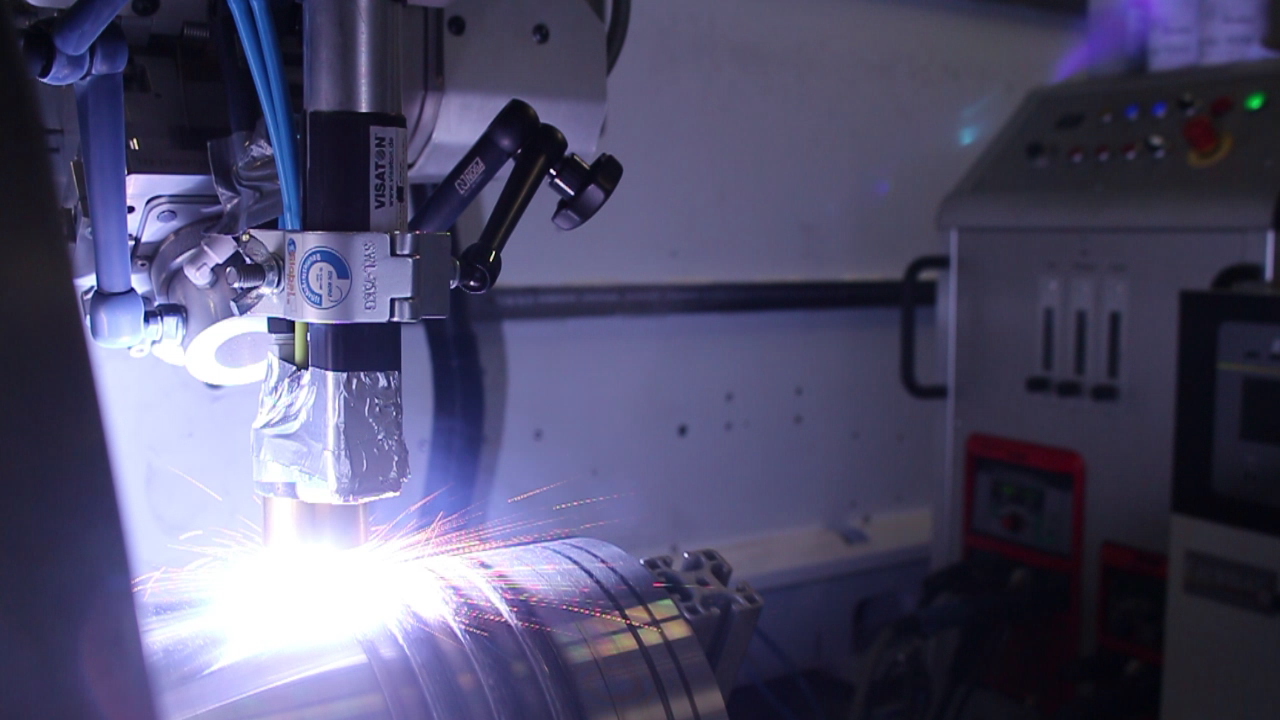
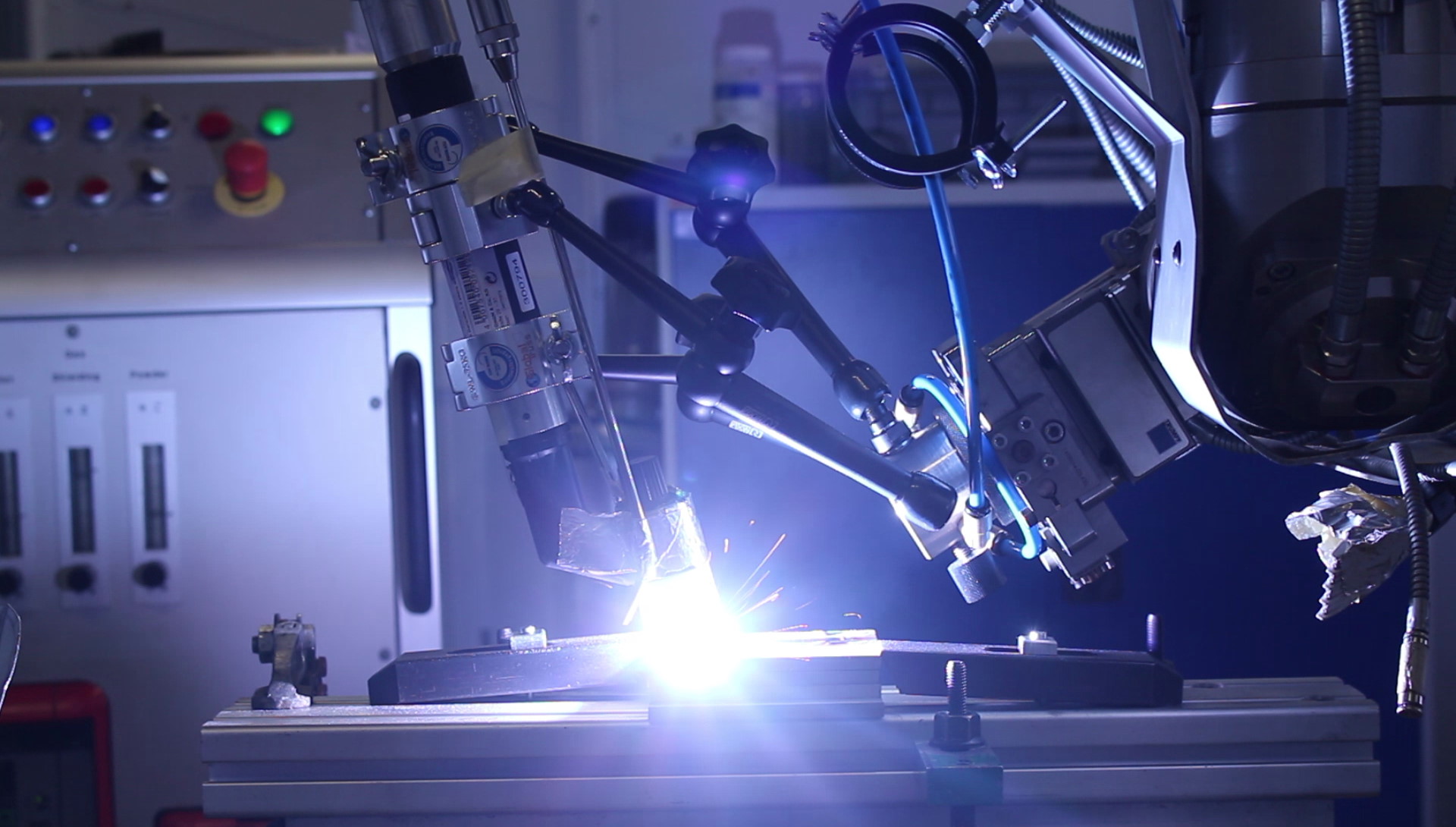
Welded joints are found everywhere in everyday life: when you open the car door, laser-welded seams hold the metal sheets together; when you turn on the heating, energy from wind turbines is used; and even when you load the washing machine. There, a resistance-welded cross seam holds the drum together. No matter where you look: Welded seams are responsible for secure, inseparable connections between metallic materials.
Coatings applied by laser powder deposition (LPA) are making their way into our lives as wear-resistant coatings on industrial tools. And additive manufacturing using 3D printing processes, such as directed energy deposition, has become an integral part of prototyping. Complex structures can be produced at high build rates.
Many of the processes have been known for a long time and have been continuously developed. As part of Industry 4.0, welding technology is also developing in innovative leaps and bounds.
Major welding technologies include
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Processes
- Manual Metal Arc Welding and
- Laser or Laser Hybrid Welding
- Vacuum electron beam welding
- Not to mention resistance spot welding
Welding plays a central and irreplaceable role in today's manufacturing. In addition to maximizing efficiency, the focus is also on environmental protection. Resource-saving production, sustainable CO2 footprints and recyclable long-term solutions are being demanded from all sides.
Fortunately, welding technology in particular offers many opportunities to optimize processes toward greater climate neutrality. Initiatives that utilize the latest high-strength steels in lightweight construction and enhance them with digital simulation approaches save not only resources, but also costs.
Additive manufacturing can make a direct contribution to climate protection by repairing rather than replacing. It saves costs and materials, which has a positive impact on the company's balance sheet and the environment.
High-tech materials can be produced in powder or wire form and welded to broken tool edges or damaged gas turbine blades, for example.
In order to make the best use of modern welding processes, a large number of process and material parameters must be optimally coordinated. The constant confrontation with current issues in the industry leads to continuous development. We can supply what our industrial partners need, or we can develop completely new solutions together.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Production Systems and Design Technology
Fraunhofer Institute for Production Systems and Design Technology